Alternative Name(s): Cluster of Differentiation 138
Test Description
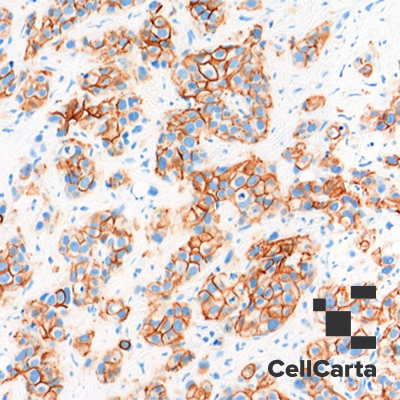
CD138 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily and is mainly expressed on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, activated B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, but it is also found on resting monocytes and dendritic cells. CD138 is involved in a variety of diseases, including cancer, and demonstrates strong anti-tumor properties. Many tumors are refractory to treatment with anti-PD-1 or anti-CD138 as single therapy; thus the combination of PD-1 and CD138 is a promising new antitumor treatment.