Alternative Name(s): Cleaved Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase
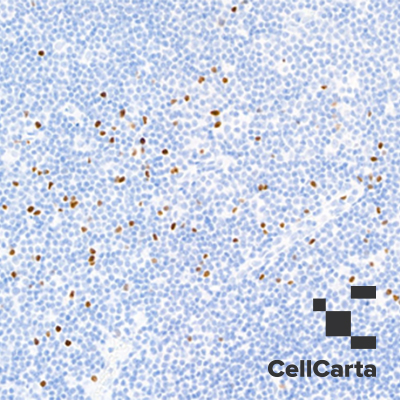
Test Description
cPARP is a 116 kDa nuclear poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase involved in DNA repair in response to environmental stress. cPARP can be cleaved in vitro by many ICE-like caspases, and it is one of the main cleavage targets of caspase-3 in vivo. Human cPAPR cleavage occurs between Asp214 and Gly215, separating the PARP amino-terminal DNA-binding domain (24 kDa) from the carboxy-terminal catalytic domain (89 kDa). cPARP helps cells maintain their viability; its cleavage facilitates cellular disassembly and serves as a marker of cells undergoing apoptosis.