Alternative Name(s): FLT-1
Test Description
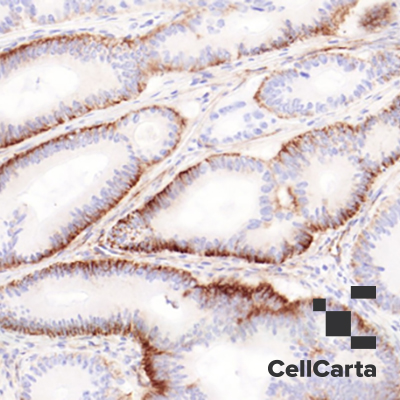
VEGF Receptor 1 is a 180 kDa receptor tyrosine kinase expressed in vascular endothelial cells, placental trophoblast cells, and peripheral blood monocytes. VEGFR1 plays an important role in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. The protein acts as a receptor for VEGF, VEGFB, and PLGF. An alternatively spliced form of the gene produces a soluble protein (sFLT1), which binds vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with high affinity. sFlt1 has a higher affinity for VEGF indicating that it may function as an inhibitor in the VEGF response. VEGF is thought to be important for the development of embryonic vasculature and may function as a tumor angiogenesis factor. It has been shown that an alternatively spliced form of FLT1 produces a soluble protein, termed sFLT1, which binds vascular endothelial growth factor with high affinity. As sFLT1 has a higher affinity for VEGF than FLK1, it may function as an inhibitor of VEGF response.